
Breast Augmentation
Having beautiful and shaped breasts is undoubtedly something that many women desire. For this reason, many women prefer breast augmentation today.
Who is breast augmentation performed for?
For
those who have small breasts since puberty
Post
-pregnancy or patients who lose significant amounts of weight
Patients
who have lost their breasts as a result of breast cancer
In
congenital diseases, patients with no breast, small or asymmetrical
Patients
who are uncomfortable with their breast size and want to have larger breasts
Surgery is performed for more symmetrical, voluminous, fuller and upright breasts.
The most suitable and healthy solution for breast smallness is silicone breast prosthesis. Augmentation procedures with adipose tissues taken from the person can also be tried, but they are generally not preferred as they may melt and cause a decrease in volume. The most suitable patients for breast augmentation with fat injection are those with a high body fat percentage. At the same time, the amount of regional fat is also reduced in this way.
How are the prostheses used in breast augmentation operations?
Silicone prostheses are of 2 types: drop (anatomical) and round. The suitability of the prosthesis is decided according to the person's chest structure, neck, shoulder-body relationship, breast skin, the patient's request and the situation that the surgeon deems appropriate. The outer wall of breast prostheses consists of a silicone sheath. They are products that contain silicone gel. The walls are rough or smooth surfaced. It is available in different sizes in terms of volume, base diameter and height.
The probability of any health problems in breast augmentation surgery performed with FDA-approved, state-of-the-art prostheses is very low. Studies have not found a relationship between silicone prosthesis and breast cancer. Breast prostheses are used for many years. They do not need to be replaced unless a problem occurs.
Can people who have had breast augmentation surgery breastfeed?
This question is one of the most frequently asked questions by women. For this reason, many young women who have not become mothers hesitate to have breast augmentation surgery. However, studies have shown that the applied prosthesis does not interfere with breastfeeding.
How is breast augmentation surgery done?
The operation takes 1-2 hours. The patient is discharged on the same day or after staying in the hospital overnight.
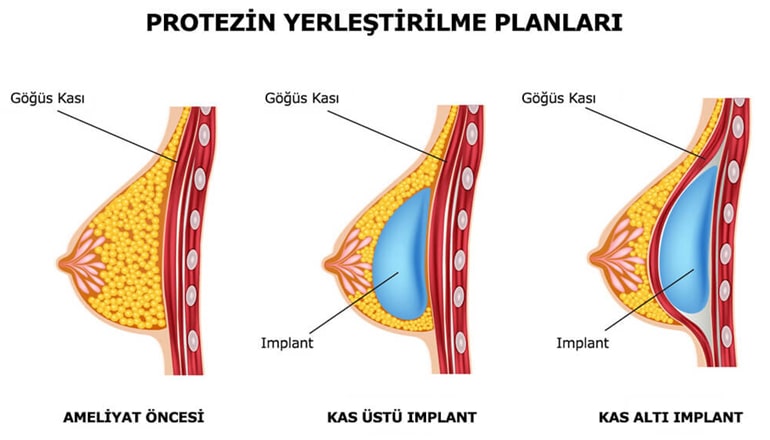
Silicone prostheses are placed on the breast with 3 methods, sub-muscular (pectoralis major muscle), supramuscular or both sub-muscular and supramuscular (Dual plane) according to the place of placement on the breast.
The prosthesis is most often placed in the inframammary fold, less often around the nipple, armpit or navel area.
Very slight breast sagging is also eliminated with breast augmentation surgeries. However, it is useful to include breast lift surgeries in moderate and advanced sagging.
What are the points to be considered in the postoperative period?
It is possible to experience pain in the first 2 days, which is a little more in the prosthesis placed under the muscle, but can be reduced with the painkillers to be given in the prosthesis surgeries. Swelling and bruises are seen in and around the breast area. They usually disappear within 2 weeks. However, it takes a period of 6 months to 1 year for the swelling in the breast to completely go down and the breast to take its final shape.
If the person does not do heavy work in the postoperative period, he/she returns to his/her work and normal life after 3 days. It is recommended to avoid heavy exercises and lifting weights for about a month.
What are the risks that may occur with the surgery?
Bleeding and infection due to surgery are rare but can be seen. Some patients may have decreased or increased sensory changes in the nipples. This condition is usually temporary.
Against the prosthesis, the body produces a membranous substance called a capsule. This membrane, in its thin form, does not cause any problems. However, this capsule may reach moderate and advanced size in some patients. In this case, a secondary intervention may be required.
The possibility of rupture of the prosthesis is not possible except in cases of serious chest trauma such as in-vehicle traffic accident, falling from a height and sharp object injuries.